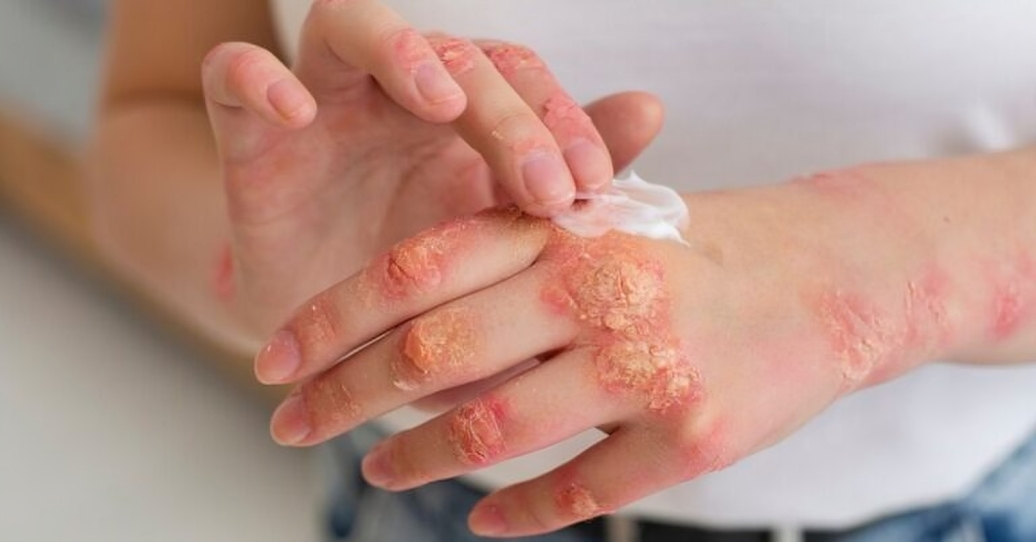
In the realm of dermatological conditions, Blisterata stands out as a unique and often challenging skin disorder. Characterized by the formation of blisters on the skin’s surface, this condition can affect individuals of all ages, leading to discomfort and potential complications if not properly managed. This comprehensive guide aims to explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures for Blisterata, providing valuable insights for patients and healthcare providers alike.
What is Blisterata?
The dermatological disorder known as blisterrata is characterized by the development of fluid-filled blisters on the skin. Depending on the underlying reason, these blisters might vary in size and appear on various regions of the body. Numerous things, including infections, allergies, autoimmune diseases, and genetic predispositions, may cause blisters.
Causes of Blisterata
The development of Blisterata can be attributed to several potential causes, including:
- Infections: Viral infections such as herpes simplex and chickenpox can lead to blister formation. Bacterial infections like impetigo can also result in blisters.
- Allergic Reactions: Contact with allergens, such as poison ivy or certain chemicals, can cause an allergic reaction that manifests as blisters.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid involve the immune system attacking healthy skin cells, resulting in blistering.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing blistering skin conditions.
Symptoms of Blisterata
The primary symptom of Blisterata is the presence of blisters on the skin. These blisters may be accompanied by:
- Redness and Swelling: The affected area may appear red and swollen, indicating inflammation.
- Pain and Itching: Blisters can be painful or itchy, leading to discomfort and potential risk of infection if scratched.
- Fluid Discharge: In some cases, blisters may rupture, releasing clear or yellowish fluid.
- Crusting and Scabbing: As blisters heal, they may form crusts or scabs, which eventually fall off as new skin forms.
Diagnosis of Blisterata
Diagnosing Blisterata involves a thorough examination by a dermatologist, who may perform the following assessments:
- Physical Examination: The dermatologist will inspect the blisters and surrounding skin to assess their appearance and distribution.
- Medical History: A detailed medical history will help identify potential triggers or underlying conditions contributing to the blistering.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a skin biopsy may be conducted to examine a sample of the affected skin under a microscope, aiding in the diagnosis of autoimmune or genetic causes.
Treatment Options for Blisterata
Effective management of Blisterata requires a tailored approach based on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Treatment options include:
- Topical Medications: Corticosteroid creams or ointments can reduce inflammation and alleviate itching. Antibiotic ointments may be prescribed if there is a risk of infection.
- Oral Medications: For more severe cases, oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressive drugs may be necessary to control the immune response.
- Antiviral or Antibiotic Therapy: If an infection is identified as the cause, appropriate antiviral or antibiotic medications will be prescribed.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding known allergens and irritants, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and maintaining proper skin hygiene can help manage symptoms.
Preventive Measures for Blisterata
Preventing the recurrence of Blisterata involves adopting proactive measures to protect the skin and minimize exposure to potential triggers:
- Identify Triggers: Keeping a diary of activities, foods, and products that precede blister outbreaks can help identify potential triggers to avoid.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing protective clothing and gloves can prevent contact with allergens and irritants.
- Skin Care Routine: Establishing a gentle skincare routine that includes moisturizing can help maintain the skin’s integrity and reduce the risk of blistering.
- Sun Protection: Applying sunscreen and wearing protective clothing when outdoors can prevent sunburn-related blistering.
Living with Blisterata
Although having blisters may be difficult, people can have happy, meaningful lives if they get the right care and assistance. A thorough treatment plan that is customized to each patient’s requirements must be developed in close collaboration with healthcare professionals. Counseling and support groups may also provide practical guidance and emotional support for coping with the condition’s effects on day-to-day living.
Conclusion: Embracing a Life with Blisterata
Even though blisters are a complicated dermatological problem, they may be efficiently treated with the appropriate care. Through knowledge of the condition’s origins, symptoms, and available treatments, people may proactively reduce their suffering and avoid recurrence. For patients afflicted with blepharitis, there is hope for new medicines and a higher quality of life thanks to continuous research and breakthroughs in dermatology.